| |
 |
|
| |
COBOL TUTORIAL
FOR BCA STUDENTS OF M G UNIVERSITY |
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
Basic operations on a file involve the reading and
writing of its records.
When the file is sequential, there are three verbs
for the purpose. These are READ, WRITE and REWRITE.
|
|
| |
|
| |
We know that the processing of a file should begin
with the execution of an OPEN statement. A file
can be opened in any one of the four open modes
– INPUT, OUTPUT, EXTEND and I-O. The following
is the syntax (simplified) of the OPEN statement:
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
The CLOSE statement terminates the processing of the
file. The following is the syntax (simplified) of
the CLOSE statement:
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
A READ statements reads a record of the file. The
file must be open in either the INPUT or I-O mode.
The syntax of READ statement is as follows:
|
|
| |
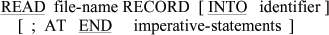
|
|
| |
|
| |
As a result of the execution of the WRITE statement,
the record is released from the record area and is
written onto the file. The WRITE statement for tape
and sequential-disk files has the following syntax:
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
The REWRITE statement is used to update an existing
record in the disk file. The general format is as
follows:
|
|
| |

|
|
| |
It may be noted that the syntax is similar to that
in the case of a WRITE statement and the FROM option
has the same meaning. There should be a valid READ
statement before the execution of the REWRITE statement.
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
|
