| |
 |
|
| |
COBOL TUTORIAL
FOR BCA STUDENTS OF M G UNIVERSITY |
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| |
The
purpose of this verb is to make available the next
logical record from an input file. It is important
to note the meaning of "next" logical record
in the above statement. The first time the READ statement
is executed, the first record of the file will be
read into the record area described in the FILE SECTION
of the DATA DIVISION. The next time the READ statement
is executed, the second record will be read in the
same area. In this way each time a READ statement
is executed the successive records will be read in
the same area. Thus a time will come when there will
be no more records in the file. In that case the statements
following the AT END clause will be executed.
The format of the READ statement is:
|
|
| |
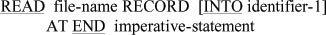 |
|
| |
Example:
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
As a result of this statement, normally the next record
from the OLD-MASTER file will be read. If there is
no more record in OLD-MASTER, the value zero will
be moved to the field named END-OF-RECORDS.
|
|
| |
|
| |
This example is similar to the earlier example. The
next record from the TRANSACTION file will be read
if it is available. If the file does not contain any
more records, the control will be transferred to the
paragraph named PARA-END.
|
|
| |
|
| |
This statement not only reads the next record into
the record area of CARD-FILE but also moves the record
into the area name IN-REC. When there is no more record
in the CARD-FILE, the control is transferred to the
paragraph named JOB-END. If the record area of the
CARD-FILE has been named CARD-REC, the above statement
is equivalent to
|
|
| |
|
| |
It may be noted that if the record has been successfully
read, it is now available in CARD-REC as well as IN-REC.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
|
